What causes Type 2 diabetes?
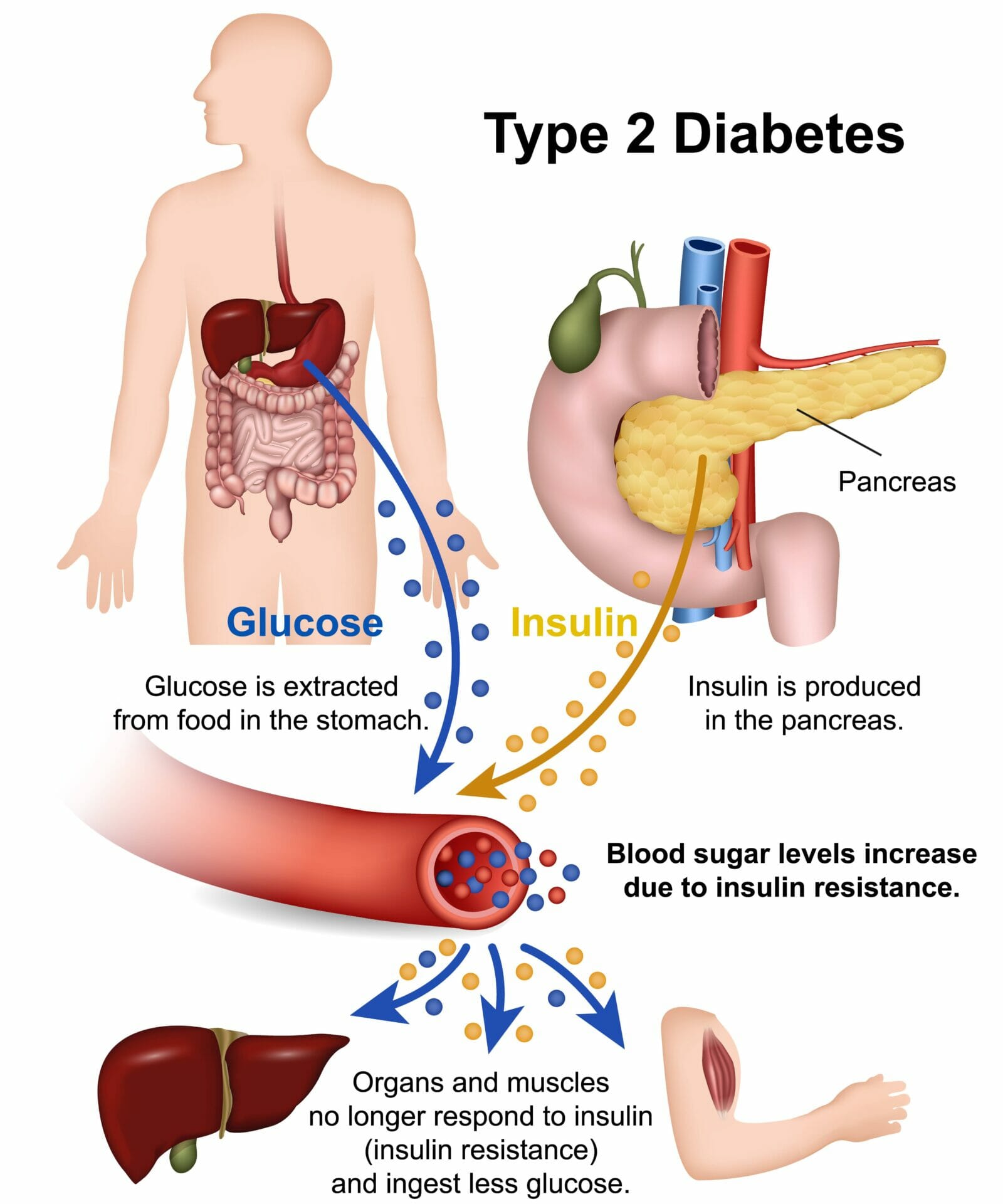
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterised by high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar properly. Insulin is a hormone that helps move glucose from the bloodstream into cells for energy.
Type 2 diabetes is a prevalent health concern worldwide, with millions of people affected by the condition. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that more than 400 million people have diabetes globally, and approximately 90% of them have type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes can have a significant impact on an individual’s health and quality of life. If left untreated or poorly managed, it can lead to various complications, including:
Heart disease
Stroke
Kidney disease
Nerve damage
Vision problems and blindness
Foot problems and amputations
Increased risk of infections
It is essential to understand the causes of type 2 diabetes to prevent its onset and manage the condition effectively.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Genetic and Family History
Genetic and family history play a significant role in the development of type 2 diabetes. If you have a close family member with diabetes, such as a parent or sibling, you may have a higher risk of developing the condition yourself. Certain genetic factors can influence the way your body processes glucose and insulin, increasing your susceptibility to developing type 2 diabetes. However, having a family history of diabetes does not mean that you will definitely develop the condition, as lifestyle factors also play a crucial role.
Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle
One of the key risk factors for type 2 diabetes is obesity. Excess body weight, especially around the waistline, can increase insulin resistance and lead to elevated blood sugar levels. A sedentary lifestyle, characterised by a lack of physical activity, is also closely associated with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Regular exercise helps to maintain a healthy weight, improves insulin sensitivity, and lowers blood sugar levels.
Poor Dietary Choices
Poor dietary choices can significantly contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugary beverages, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance. On the other hand, a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help prevent or manage type 2 diabetes. Making healthier food choices and practicing portion control is essential for maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Other Contributing Factors
While genetics, obesity, and poor dietary choices are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes, there are also other contributing factors to consider:
Age: The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases with age. Most cases are diagnosed in individuals over the age of 45, although it is becoming more prevalent in younger age groups due to increasing obesity rates.
High blood pressure: Having high blood pressure is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes: Women who have had gestational diabetes during pregnancy have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS, a hormonal disorder, are at a higher risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
It’s important to note that while these factors increase the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, they do not guarantee its development. Making positive lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a balanced diet, can significantly reduce the risk and help manage the condition effectively.
Insulin Resistance and Beta Cell Dysfunction
Understanding Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. It occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance prevents glucose from entering the cells efficiently, leading to increased levels of sugar in the blood.
Several factors contribute to insulin resistance, including:
- Obesity: Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, is strongly linked to insulin resistance.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can contribute to insulin resistance.
- Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to insulin resistance.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can increase the risk of insulin resistance.
Impaired Beta Cell Function
Beta cells are responsible for producing and releasing insulin in the pancreas. In individuals with type 2 diabetes, beta cells may become impaired and fail to produce enough insulin or produce insulin that is less effective in regulating blood sugar.
Several factors can contribute to impaired beta cell function, including:
Chronic Hyperglycemia: Prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels can damage beta cells over time.
Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the body can affect beta cell function.
Genetic Factors: Some genetic variants can increase the risk of impaired beta cell function.
Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance can put additional strain on beta cells, leading to their dysfunction.
Understanding the mechanisms behind insulin resistance and beta cell dysfunction is crucial in managing and preventing type 2 diabetes. By addressing these factors through lifestyle changes, medication, and other interventions, individuals can work towards better blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
For more information on the causes and management of type 2 diabetes, you can visit this Wikipedia page.
Role of Genetics in Type 2 Diabetes
Genetic Factors and Susceptibility
While lifestyle factors play a significant role in the development of type 2 diabetes, genetics also contribute to an individual’s susceptibility to the disease. Several genetic factors have been identified that can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes:
1. Family History: Having a family history of type 2 diabetes increases the likelihood of developing the condition. Close relatives, such as parents or siblings, with type 2 diabetes can significantly impact an individual’s risk.
2. Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asians, have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to other populations. This suggests that genetics may play a role in susceptibility among different ethnic backgrounds.
3. Genetic Variants: Research has identified specific genetic variants that are associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. These variants can affect insulin secretion, insulin action, and other factors involved in glucose metabolism.
Monogenic Forms of Diabetes
In addition to the more common form of type 2 diabetes, known as polygenic type 2 diabetes, there are also monogenic forms of diabetes that are caused by mutations in a single gene. These mutations can affect insulin production and lead to problems with glucose regulation.
1. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY): MODY is a rare form of diabetes that usually occurs before the age of 25. It is caused by mutations in specific genes that regulate insulin production. MODY is often misdiagnosed as type 1 or type 2 diabetes, but genetic testing can help differentiate it.
2. Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus (NDM): NDM is a rare form of diabetes that is diagnosed in the first six months of life. It is caused by genetic mutations that affect insulin production. NDM requires lifelong treatment with insulin.
These monogenic forms of diabetes are relatively rare compared to polygenic type 2 diabetes but highlight the importance of genetics in understanding the disease. Further research is needed to fully understand the role of genetics in type 2 diabetes and develop targeted treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup.
It’s fascinating to see how both genetic and lifestyle factors contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and work towards preventing or managing the disease.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
One of the primary risk factors for type 2 diabetes is obesity. Obesity is characterised by excessive body weight, typically resulting from a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, can increase insulin resistance and lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. Studies have shown that individuals with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Physical Inactivity and Sedentary Lifestyle
Leading a sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity are significant contributors to the development of type 2 diabetes. Regular physical activity helps to regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and maintain a healthy weight. Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle can lead to weight gain, increased insulin resistance, and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It is important to incorporate regular exercise and physical activity into daily routines to reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Dietary Factors and Type 2 Diabetes
Diet plays a crucial role in the development of type 2 diabetes. A diet high in refined carbohydrates, sugary beverages, saturated and trans fats, and low in fibre can increase the risk of developing the disease. These dietary factors can contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and impaired glucose metabolism. On the other hand, a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Other Environmental Contributors
In addition to lifestyle factors, certain environmental factors can also contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Some of these factors include:
Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to obesity, insulin resistance, and high blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Smoking: Smoking has been associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, as it can lead to insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism.
Exposure to Chemicals: Certain environmental toxins and chemicals, such as certain pesticides and pollutants, have been linked to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Understanding these lifestyle and environmental factors can help individuals make healthier choices and reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and managing stress levels, individuals can decrease their risk of developing this chronic condition.
Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes
Defining Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that occur together, increasing the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, stroke and type 2 diabetes. The main factors that contribute to metabolic syndrome include:
1. Obesity: Excess fat, particularly around the waistline, is a significant risk factor for metabolic syndrome.
2. Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
3. High Blood Pressure: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is often associated with metabolic syndrome.
4. Dyslipidemia: This refers to abnormal levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, typically characterized by high levels of LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) and low levels of HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol).
5. Elevated Blood Sugar: Increased levels of glucose in the blood, which can be a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Relationship Between Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes
There is a strong link between metabolic syndrome and the development of type 2 diabetes. Having metabolic syndrome increases the risk of developing insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels, both of which are key factors in the development of type 2 diabetes. In fact, individuals with metabolic syndrome are five times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes compared to those without the syndrome.
The underlying mechanisms connecting metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes are complex and not fully understood. However, it is believed that the combination of insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and obesity contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes in individuals with metabolic syndrome.
It is important to note that not everyone with metabolic syndrome will develop diabetes. Lifestyle factors, such as diet and physical activity, play a significant role in the progression from metabolic syndrome to type 2 diabetes. By making healthy lifestyle choices, including maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing weight, individuals can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
To learn more about metabolic syndrome and its connection to type 2 diabetes, you can refer to the Metabolic Syndrome Wikipedia page.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a complex condition with various factors that contribute to its development. While genetics play a role, lifestyle choices, such as diet and physical activity, are key determinants of the disease. The condition occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. These include being overweight or obese, having a sedentary lifestyle, having a family history of the disease, and being of certain ethnicities, such as African American, Hispanic, or Native American.
It is essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle and make conscious choices to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress levels, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are also crucial for early detection and management of the disease.
By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with type 2 diabetes, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent or manage the condition. With proper lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, individuals with type 2 diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021, March 25). Type 2 Diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type2.html
American Diabetes Association. (n.d.). Type 2 Diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/type-2
Mayo Clinic. (2021, July 10). Type 2 Diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-2-diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20351193