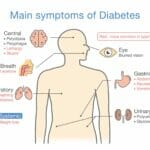
Diabetic neuropathy: a common complication of diabetes that affects the nerves, leading to various symptoms and complications. It is estimated that around 50% of people living with diabetes develop some form of neuropathy during their lifetime.
What is Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy refers to a serious nerve damage that occurs as a result of long-term high blood sugar levels in individuals living with diabetes. The condition affects various parts of the body, including the peripheral nerves, autonomic nerves and cranial nerves. The peripheral nerves that are most commonly affected include those in the hands or feet, legs and arms.
The symptoms of diabetic neuropathy can range from mild to severe and may include:
Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
Loss of sensation or feeling in the affected areas
Sharp or burning pain
Muscle weakness
Problems with coordination and balance
Digestive issues
Bladder problems
Sexual dysfunction
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of diabetic neuropathy is still not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of factors, including:
Prolonged high blood sugar levels
Damage to blood vessels that supply the nerves
Inflammation in the nerves
Genetic factors
Certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing diabetic neuropathy, including:
Duration of diabetes
Poorly controlled blood sugar levels
Obesity
High blood pressure
Smoking
High cholesterol levels
It’s important for individuals living with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels effectively and to undergo regular check-ups to monitor for any signs or symptoms of neuropathy. Early detection and treatment can help prevent the progression of the condition and reduce the risk of complications.
For more information on diabetic neuropathy, visit Diabetes.co.uk.
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy
There are different types of diabetic neuropathy, each affecting different parts of the body. Understanding these types can help individuals living with diabetes manage their symptoms more effectively. Here are the four main types of diabetic neuropathy:
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy: is the most common type of diabetic neuropathy, affecting the peripheral nerves that control sensation and movement in the arms, legs, hands, and feet. Symptoms may include numbness, tingling, pain, and weakness in the affected areas. It typically affects both sides of the body.
Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy: affects the nerves that control involuntary bodily functions such as digestion, heart rate and blood pressure. This type of neuropathy can cause symptoms like dizziness, digestive issues, bladder problems and sexual dysfunction.
Proximal Neuropathy
Proximal neuropathy: also known as diabetic amyotrophy, affects the nerves in the thighs, hips, buttocks, and legs. This type of neuropathy can cause severe pain, weakness and difficulty moving the affected limbs.
Focal Neuropathy
Focal neuropathy: affects a specific nerve or group of nerves and can occur in any part of the body. This type of neuropathy can cause sudden weakness or pain in specific areas, such as the head, torso, or leg. The symptoms of focal neuropathy usually occur suddenly and may improve over time.
Understanding the different types of diabetic neuropathy is important for managing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment. If you suspect you have diabetic neuropathy, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy can cause a range of symptoms that vary from person to person. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Numbness and Tingling
One of the first signs and symptoms of diabetic neuropathy is numbness and tingling in the hands, feet and legs. This sensation is often described as a “pins and needles” feeling and can be quite uncomfortable. It is important to note that this loss of sensation can increase the risk of injuries, as individuals may not notice when they have hurt themselves.
Burning or Shooting Pain
Many people with diabetic neuropathy experience a burning or shooting pain in the affected areas. The pain can be intermittent or constant and may worsen at night. This pain can greatly impact a person’s quality of life and make everyday tasks more difficult to perform.
Muscle Weakness and Loss of Balance
Diabetic neuropathy can also lead to muscle weakness and a loss of balance. This can make walking and other physical activities challenging, increasing the risk of falls and injuries. It is important for individuals with diabetic neuropathy to take precautions and seek proper medical care to manage these symptoms.
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of these symptoms, as they can provide guidance and recommendations for managing diabetic neuropathy. Additionally, maintaining good blood sugar control through proper diabetes management is essential in preventing and managing the progression of neuropathy.
For more information on diabetic neuropathy and its symptoms, visit Diabetes.org.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Neuropathy
When it comes to managing diabetic neuropathy, there are several treatment options available that can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life. Here are some common treatment approaches for diabetic neuropathy:
Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial in managing diabetic neuropathy. By keeping blood sugar levels within a healthy range, it can help prevent further nerve damage and alleviate symptoms. This can be achieved through:
Regular monitoring: Checking blood sugar levels regularly and adjusting medication and lifestyle accordingly.
Healthy diet: Following a balanced diet that is low in sugar and carbohydrates can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and promote stable blood sugar levels.
Medications for Pain and Symptom Management
There are various medications available that can help manage the pain and symptoms associated with diabetic neuropathy. These may include:
Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provide temporary relief from mild to moderate pain.
Antidepressants: Certain antidepressant medications, such as tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SSNRIs), can help alleviate nerve pain associated with diabetic neuropathy.
Anticonvulsants: Certain anticonvulsant medications, such as gabapentin and pregabalin, can help manage nerve pain.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable medication and dosage for individual needs.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Engaging in regular physical therapy and exercise can help improve strength, flexibility, and circulation, which can alleviate symptoms of diabetic neuropathy. Physical therapy may include:
Stretching exercises: Stretching can help improve flexibility and reduce muscle stiffness associated with neuropathy.
Low-impact exercises: Activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling can help improve cardiovascular health and promote overall well-being.
Balance and coordination exercises: Practicing balance and coordination exercises can help reduce the risk of falls and improve mobility.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise program to ensure safety and effectiveness. Treatment options for diabetic neuropathy may vary depending on individual circumstances, so it is important to work closely with a healthcare team to develop a personalised treatment plan.
Prevention and Management of Diabetic Neuropathy
Routine Foot Care
Foot care is essential for individuals living with diabetic neuropathy, as they are more prone to foot problems and infections due to reduced sensation and poor circulation. Here are some important foot care tips to follow:
Inspect your feet daily: Check for any cuts, sores, blisters, or other abnormalities on your feet. If you have trouble seeing or reaching your feet, ask a family member or use a mirror.
Wash your feet daily: Use warm water and a mild soap to clean your feet. Dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal infections.
Moisturise your feet: Apply a moisturiser to prevent dry skin, but avoid applying it between the toes, as it can increase the risk of fungal infections.
Trim your nails carefully: Cut your toenails straight across and file any sharp edges to avoid ingrown toenails.
Avoid walking barefoot: Always wear shoes or slippers to protect your feet from injury.
Regular Check-ups and Monitoring
Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are crucial for managing diabetic neuropathy effectively. Here are some key aspects of monitoring and managing the condition:
Regular foot exams: Schedule regular foot exams with a podiatrist to detect any signs of foot problems early on.
Blood sugar monitoring: Keep track of your blood sugar levels regularly and follow your healthcare professional’s recommendations for maintaining good control.
Blood pressure and cholesterol management: High blood pressure and cholesterol can further damage nerves and blood vessels. Work with your healthcare professional to manage these conditions effectively.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
In addition to specific measures for foot care and medical management, maintaining a healthy lifestyle overall can help prevent and manage diabetic neuropathy. Here are some lifestyle factors to consider:
Eating a balanced diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-fat foods.
Regular exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve blood circulation, control blood sugar levels, and maintain a healthy weight. Consult your healthcare professional before starting any exercise program.
Smoking cessation: If you smoke, quitting is crucial to improve overall health and reduce the risk of complications from diabetic neuropathy.
By following these preventive measures and incorporating healthy habits into your daily routine, you can effectively manage diabetic neuropathy and reduce the risk of complications. Consult with your healthcare professional for personalized guidance and recommendations.
Complications of Diabetic Neuropathy
Foot Ulcers and Infections
One of the most common complications of diabetic neuropathy is the development of foot ulcers and infections. Nerve damage can lead to a loss of sensation in the feet, making it difficult for individuals with diabetes to detect cuts, blisters, or sores on their feet. Without proper care, these minor injuries can develop into ulcers, which can become infected and lead to more serious complications. It is crucial for individuals with diabetic neuropathy to pay close attention to their feet and seek medical attention promptly if they notice any signs of infection or non-healing wounds. Wearing appropriate footwear and practicing good foot hygiene can also help prevent foot ulcers and infections.
Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis is a condition that affects the movement of food through the digestive system. It occurs when nerve damage disrupts the normal functioning of the stomach muscles, leading to delayed or incomplete emptying of the stomach. This can cause symptoms such as nausea, bloating, vomiting, and poor appetite. Individuals with diabetic neuropathy are at an increased risk of developing gastroparesis, as high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves that control the stomach. Managing blood sugar levels and making dietary changes, such as eating smaller meals more frequently, can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Sexual Dysfunction
Diabetic neuropathy can also affect sexual function in both men and women. Nerve damage can result in reduced sensation and blood flow to the genitals, leading to difficulties with arousal, erectile dysfunction in men, and decreased lubrication and difficulties reaching orgasm in women. These issues can have a significant impact on the quality of life and relationships. It is important for individuals experiencing sexual dysfunction to discuss their symptoms with a healthcare provider, as there are treatment options available that can help improve sexual function.
Managing diabetic neuropathy is essential in preventing or minimising these complications. Regular medical check-ups, maintaining good blood sugar control, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and following the treatment plan prescribed by a healthcare provider are key steps in managing and preventing complications associated with diabetic neuropathy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetic neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. It is essential for individuals living with diabetes to understand the risk factors and symptoms of diabetic neuropathy, as well as seek proper medical care and management strategies.
Diabetic neuropathy can affect various parts of the body, including the feet, legs, hands and internal organs. The damage to the nerves can lead to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, pain, muscle weakness, and problems with coordination and balance.
Managing diabetic neuropathy involves a multimodal approach that includes proper blood sugar control, regular physical activity, a healthy diet, and medications to relieve symptoms and slow down nerve damage. In some cases, additional treatments such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and alternative therapies may be beneficial.
It is crucial for individuals living with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a comprehensive management plan for diabetic neuropathy. Regular check-ups and monitoring of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels are essential to prevent or delay the progression of neuropathy.
Educating oneself about the condition and being proactive in self-care is also crucial. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
By taking appropriate measures to manage diabetes and diabetic neuropathy, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and maintain a good quality of life. With proper medical care, lifestyle modifications, and support from healthcare professionals, individuals with diabetic neuropathy can lead fulfilling and healthy lives.
Remember, if you have any symptoms of diabetic neuropathy or are concerned about your overall health, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance on managing the condition.